Photoelectric Effect
Photoelectric Effect: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Photoelectric Effect, Threshold Frequency, Threshold Wavelength, Photoelectrons, Work Function, Characteristics of Photoelectric Effect, Einstein's Equation for Explanation of Photoelectric Effect, etc.
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect
The energy absorbed by each molecule of a substance is and bond energy per molecule is What will be the kinetic energy of the molecule per atom?
What do you mean by the term photoelectrons?
The photoelectric effect is the emission of _____ or other free carriers when light shines on a material.
The kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected from a metal on irradiation with light of frequency is K. When irradiated with light of frequency , the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons becomes . What is the threshold frequency of the metal?
In case of photoelectric effect, slope of vs curve is (where - stopping potential, subjected frequency)
Select the correct statement about the photoelectric experiment from the following.
Light of wavelength , shines on a metal surface with intensity , and the metal emits electrons per second of average energy . What will happen to and if is doubled?
In photoelectric effect, the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases linearly with the frequency of incident light.
A zinc ball of radius, charged to a potential The ball is illuminated by a monochromatic ultraviolet light with a wavelength The photoelectric threshold for zinc is The potential of ball after a prolonged exposure to the is
A certain metal has a work function of . It is irradiated first with of light and later with of light. Among the following, the correct statement is: [Given:Planck constant Speed of light ]
Ultra-violet light is shone on a zinc surface and photoelectrons are emitted. The graph shows how the stopping potential varies with frequency
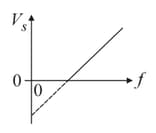
Planck's constant may be determined from the charge of an electron multiplied by
A light of frequency when falls on a metal plate emits electrons that have double the kinetic energy compared to the kinetic energy of emitted electrons when frequency of falls on the same plate. The threshold frequency of the metal in is
If the work function for Caesium atom is , find the approximate value of its threshold wavelength.
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is found to be when the metal is irradiated with radiation of frequency . The threshold frequency of the metal is:
With increasing biasing voltage of a photo diode, the photocurrent magnitude:
In photoelectric effect, the kinetic energy of the photoelectrons increases linearly with the
When the frequency of the incident radiation on a metallic plate is doubled, KE of the photolectrons will be
Photoelectric work function of a particular metal is . If a light having a wavelength of falls on the metal, then find out the approximate speed of the photoelectron emitted:
The factor on which the number of photoelectrons emitted per unit time depends in the photoelectric effect is
